A root canal infection is the inflammation of the tissues at the root of a tooth caused by bacterial infection. It develops as a result of deep cavities, trauma, or advanced gum diseases. If left untreated, it can lead to severe pain, abscess, jaw swelling, tooth loss, and serious health problems. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment methods of root canal infection. For information about post-wisdom tooth extraction infection, you can check our post-extraction infection symptoms content.
Causes of Root Canal Infection
Root canal infection can arise from various factors. The most common causes include:
- Deep tooth decay
- Trauma to the tooth
- Untreated gum problems
- Tooth fractures or cracks
- Failed or insufficient root canal treatments
- Poor oral hygiene
- Weakened immune system
Symptoms of Root Canal Infection
Root canal infection presents with easily noticeable symptoms. The main signs include:
- Severe, throbbing tooth pain, especially at night
- Sensitivity to hot and cold
- Pain or pressure while chewing
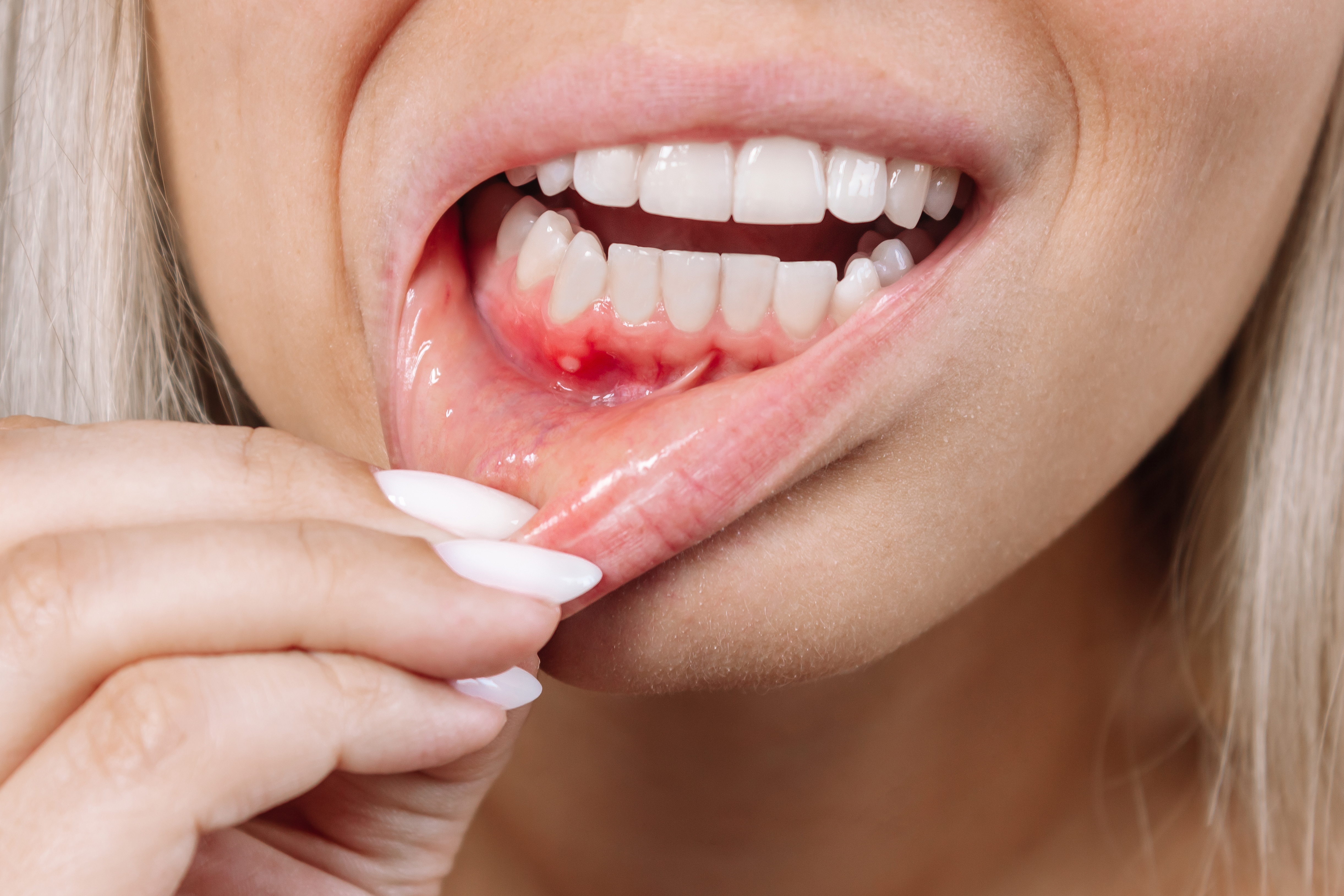
- Swelling and redness in the gums
- Swelling in the face and jaw
- Pus or discharge from the gums
- Bad taste and odor in the mouth
- Swollen or tender lymph nodes
- Loosening of the tooth in advanced cases
How is Root Canal Infection Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves clinical examination, radiographic imaging, and pulp vitality tests. The dentist checks for sensitivity by touching or tapping the suspected tooth, examines its color, gum condition, and any swelling. X-rays or CT scans identify the infection and abscess. Pulp vitality tests assess the condition of the tooth’s nerves.
Is a Tooth Infection Dangerous?
If left untreated, a tooth infection can harm surrounding tissues and overall health. Progressing infections may cause:
- Bone resorption and tooth loss
- Severe facial and neck swelling (cellulitis)
- Abscess rupture and pus discharge inside the mouth
- Serious health risks if the infection enters the bloodstream
- Increased risk of infections in organs like heart valves and kidneys
If you experience severe pain, swelling, difficulty swallowing, or fever, consult your dentist immediately. Early intervention can save the tooth and reduce complications.
How Long Does a Root Canal Infection Take to Heal?
The average healing time is 7–10 days. During this period, symptoms subside and the infection is brought under control. Full recovery requires following your dentist’s recommended treatment plan. If tooth extraction is necessary due to the infection, learn what to expect during the procedure in our tooth extraction guide.
How to Prevent Root Canal Infection
Prevention relies on proper oral care and healthy habits. Key measures include:
- Brush your teeth twice daily
- Use dental floss or interdental brushes daily
- Clean your tongue regularly
- Visit your dentist every six months for check-ups
- Have tartar removed regularly
- Avoid sugary and acidic foods
- Maintain a balanced diet
- Use mouthguards while playing sports
- Avoid nail-biting or chewing on pencils
- If you grind your teeth, use a night guard
- Treat small cavities and fractures promptly
Complications of Root Canal Infection
- Dental Abscess: Severe pain, swelling, pus
- Bone Resorption: Jawbone deterioration and tooth loss
- Sinus Infection: Spreads from the upper jaw to sinuses, causing nasal congestion and facial pain
- Ludwig’s Angina: Spreads under the tongue, blocking the airway; a medical emergency
- Sepsis: Bacteria enter the bloodstream, creating serious health risks
- Endocarditis (Rare): Bacteria reach the heart, posing significant risk
Signs that Tooth Infection is Spreading in the Body
When a tooth infection spreads, serious symptoms may occur, including:
- Noticeable swelling in the face, jaw, or neck
- Redness and tenderness in the gums
- High fever and chills
- Severe headache
- Difficulty swallowing or sore throat
- Fatigue, weakness, and general malaise
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heartbeat
These symptoms require urgent medical attention. Early treatment protects the tooth and prevents more severe health complications.

 TR
TR