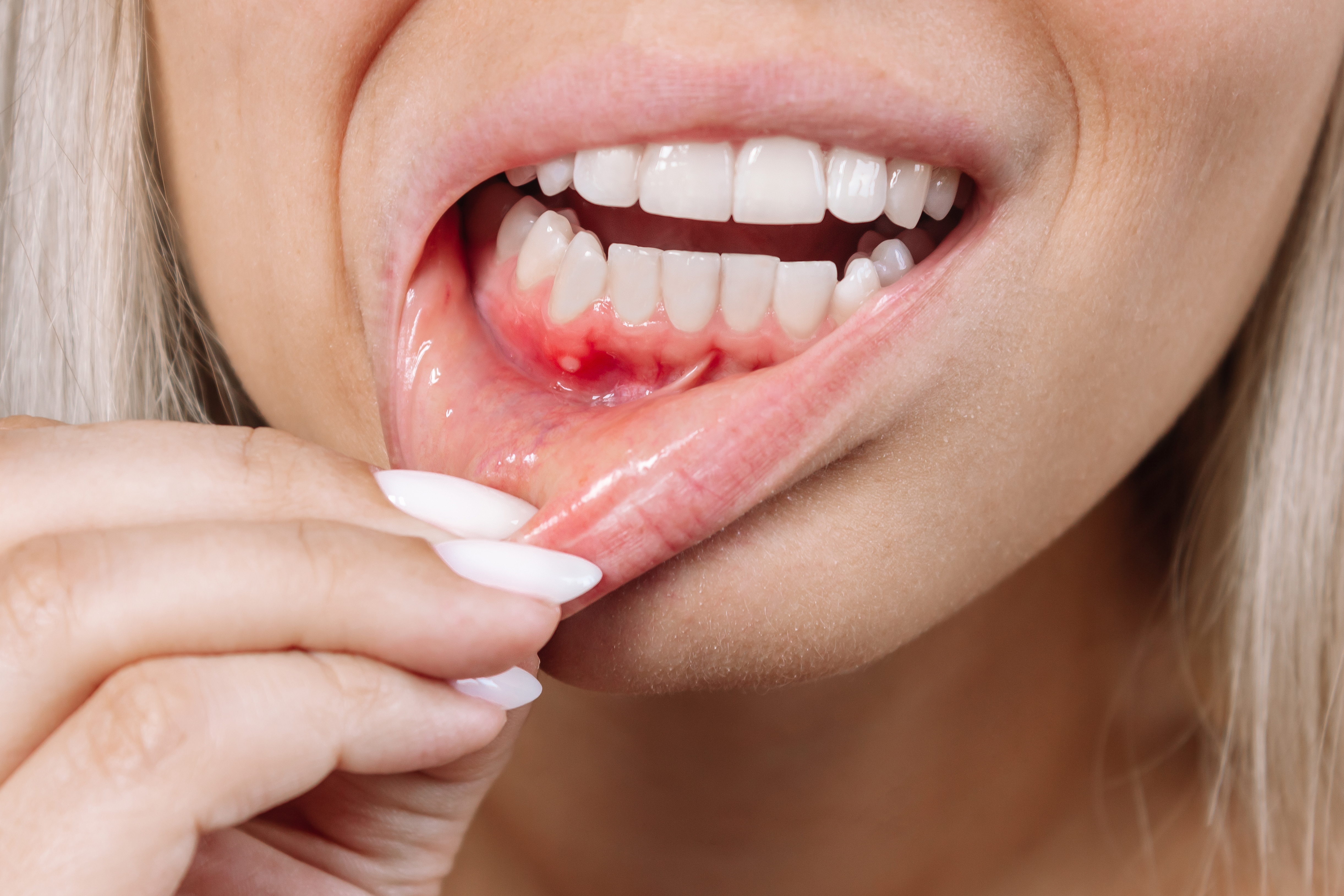
What is Gum Recession (Periodontitis)?
Gum recession (periodontitis) occurs when the edge of the gum pulls back or tissue is lost, exposing the tooth root. Although gum recession is more common in people over 40, it can also appear in younger individuals and even in children around the age of 10.
Gum recession can be observed as a change in the proportion between the crown and root of the tooth, but it does not always occur with this change. Since gum recession (periodontitis) progresses slowly, it can be difficult to notice. If left untreated, it may lead to tooth sensitivity, cavities, and in severe cases, tooth loss.
What Causes Gum Recession (Periodontitis)?
Gum recession (periodontitis) can develop due to brushing teeth too hard or incorrectly, poor oral hygiene, genetic predisposition, teeth grinding, or clenching. The causes of gum recession (periodontitis) include:
- Gingivitis or other early-stage gum inflammation
- Hard or incorrect brushing techniques
- Excessive pressure while brushing
- Teeth grinding (bruxism) or clenching
- Plaque and tartar buildup due to insufficient oral hygiene
- Incorrect fillings or dental prostheses
- Genetic predisposition
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, puberty, menopause)
- Diabetes and chronic diseases affecting the immune system
- Nutritional deficiencies (especially vitamin C deficiency)
- Stress and lack of sleep
- Incorrect or incomplete dental treatments
What Helps Gum Recession?
The most important step to improve gum recession is regular dental cleaning to prevent plaque and tartar buildup. Using the correct brushing technique, choosing a soft-bristled toothbrush, and brushing teeth gently helps protect the gums. This can prevent long-term gum recession problems.
Additional measures include:
- Using dental floss and interdental brushes
- Cleaning bacteria from between the teeth
- Using antiseptic mouthwash
- Avoiding smoking and tobacco products
These practices accelerate gum healing. Regular dental check-ups allow for early diagnosis and intervention. In advanced cases, gum grafts or flap surgery may be necessary.
Can Gum Recession (Periodontitis) Be Reversed?
If gum recession (periodontitis) is mild, treatments like dental cleaning and scaling/root planing (smoothing the root surface) can stop the problem from progressing and protect the gums. These treatments help support gum health and reduce sensitivity.
However, if gum recession is advanced, simple procedures are not sufficient. In these cases, gum surgery (flap operation) is performed to restore the lost tissue, protect tooth roots, and improve long-term gum health.
Symptoms of Gum Recession (Periodontitis)
The main symptoms of gum recession (periodontitis) include:
- Teeth appearing longer than normal
- Sensitivity to hot or cold
- Gum bleeding
- Redness or swelling of the gums
- Gaps forming between teeth
- Exposed tooth roots
- Bad breath
If you notice any of these symptoms, visiting a dentist promptly is the best way to stop progression and protect your dental health.
How is Gum Recession (Periodontitis) Treated?
Gum recession (periodontitis) treatment varies depending on the severity of the condition. In mild to moderate cases, surgical intervention is not required, and treatments such as dental cleaning, root planing (smoothing the root surface), proper oral hygiene education, and, if necessary, antiseptic mouthwash or medication are applied.
In advanced cases, flap surgery, soft tissue grafts, and bone grafts may be required. After treatment, regular dental check-ups and effective oral care are critical to prevent recurrence of the problem.
Patient Feedback After Gum Recession Surgery
Feedback from patients who underwent gum recession treatment shows that the procedure is comfortable and the results are positive. Most patients report that the surgery was easier than expected, healing progressed quickly when they followed the dentist’s recommendations, and aesthetic improvements were significant.
Patients also highlight improvements in reduced sensitivity and better chewing comfort, which directly enhances quality of life.
What is Gum Recession Surgery and How is it Done?
Gum recession surgery is preferred for patients with advanced gum recession who have esthetic or functional concerns.
- During the initial examination, a periodontology specialist determines the degree and cause of gum recession.
- The dentist and patient create a treatment plan together.
- Local anesthesia is applied to prevent pain during the procedure.
- Using the soft tissue graft method, healthy tissue from the patient’s palate or artificial graft material is transplanted to the affected area.
In some cases, instead of a soft tissue graft, a flap operation is performed. In a flap operation, the gum is lifted, the root surfaces are cleaned, and the gum tissue is repositioned.
Healing after gum recession surgery usually takes 1–2 weeks. Following the dentist’s recommendations for oral care, medication, and regular check-ups is critical for the success of the treatment.

 TR
TR